
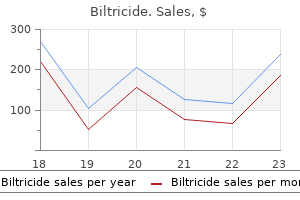
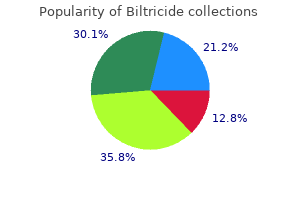
Biltricide dosages: 600 mg
Biltricide packs: 1 pills

Tics Tics are rapid symptoms of pneumonia biltricide 600mg purchase with amex, irregular, involuntary movements (motor tics) or utterances (vocal tics) that interrupt normal voluntary motor activity. They are triggered by stress, anxiety, and fatigue but may also occur at rest; they can be suppressed by a voluntary effort, but tend to re-emerge with greater intensity once the effort is relaxed. Simple vocal tics may involve moaning, grunting, hissing, clicking, shouting, throat clearing, sniffing, or coughing. Complex motor tics consist of stereotyped movements that may resemble voluntary movements. Gilles de la Tourette syndrome (often abbreviated to Tourette syndrome) is a chronic disease in which multiple motor and vocal tics begin in adolescence and progress over time. Other features of the disease are personality disturbances, obsessive-compulsive phenomena, and an attention deficit. Motor Function 68 Rohkamm, Color Atlas of Neurology © 2004 Thieme All rights reserved. Myoclonus, Tics Site of possible generators Cortical Subcortical Spinal Pattern of distribution Focal Segmental Multifocal Generalized Myoclonus Asterixis (negative myoclonus) Simple motor tic (blinking of right eye, left eye normal) Rohkamm, Color Atlas of Neurology © 2004 Thieme All rights reserved. Motor Function 69 Brain Stem Syndromes Clinical localization of brain stem lesions depends on knowledge of the tiered arrangement of cranial nerve nuclei, the intramedullary course of cranial nerve fibers, and their spatial relationship to tracts passing up and down the brain stem (see also p. Lesions can be localized to the midbrain, pons, or medulla, and further classified in terms of their location in a cross-sectional plane as anterior, posterior, medial, or lateral. The "classic" brain stem syndromes are rarely seen in actual experience, as the patterns of damage tend to overlap rather than occupy discrete areas of tissue. Brain stem lesions that affect decussating neural pathways proximal to their decussation produce crossed deficits (p. As in Wallenberg syndrome with additional ipsilateral findings: facial palsy (nuclear), rotatory vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, nystagmus, cerebellar ataxia. Skew deviation may be accompanied by the ocular tilt reaction: ipsilateral head tilt, marked extorsion of the ipsilateral eye, and mild intorsion of the contralateral eye. See-saw nystagmus is characterized by intorsion and elevation of one eye and extorsion and depression of the other. Ocular dysmetria with overreaching (hypermetria) when looking to the side of lesion and underreaching (hypometria) when looking to the opposite side.
Rakta Khakasa (Corn Poppy). Biltricide.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96527
Arrangement and Shape Can describe individual or multiple lesions: Linear (contact dermatitis such as poison ivy); annular-"ring-shaped" lesion (erythema chronicum migrans medications 5113 best 600 mg biltricide, erythema annulare centrificum, tinea corporis); iris or target lesion-two or three concentric circles of differing hue (erythema multiforme); nummular-"coin-shaped" (nummular eczema); morbilliform-"measles-like" with small confluent papules coalescing into unusual shapes (measles, drug eruption); herpetiform-grouped vesicles, papules, or erosions (herpes simplex). Primary Lesions Cutaneous changes caused directly by disease process (Table 63-1). Secondary Lesions Changes in area of primary pathology often due to secondary events. Scale is collected from advancing edge of a scaling lesion by gently scraping with side of a microscope slide or a scalpel blade. This technique can be utilized to identify hyphae in dermatophyte infections, pseudohyphae and budding yeast in Candida infections, and "spaghetti and meatballs" yeast forms in tinea versicolor. Tzanck Preparation Useful for determining presence of herpes viruses (herpes simplex virus or herpes zoster virus). Culture or immunofluorescence testing must be performed to identify the specific virus. Patch: A large (>2 cm) flat lesion with a color different from the surrounding skin. Plaque: A large (>1 cm), flat-topped, raised lesion; edges may either be distinct. Note: the presence of pustules does not necessarily signify the existence of an infection. Wheal: A raised, erythematous, edematous papule or plaque, usually representing short-lived vasodilatation and vasopermeability. Sites may be erythematous, hypopigmented, or hyperpigmented depending on their age or character. Initially, there is a single 2- to 6-cm annular salmon-colored patch (herald patch) with a peripheral rim of scale, followed in days to weeks by a generalized eruption involving the trunk and proximal extremities. Lichen Planus Disorder of unknown cause; can follow administration of certain drugs and in chronic graft-versus-host disease; lesions are pruritic, polygonal, flat-topped, and violaceous. Allergic Contact Dermatitis A delayed hypersensitivity reaction that occurs after cutaneous exposure to an antigenic substance.
Lishman (1986 medicine wheel biltricide 600 mg buy discount online, 1990) suggested that the WernickeKorsakoff lesion (see below) may sometimes itself be responsible for pictures of dementia by encroaching on key neurochemical nuclei at the base of the brain, with consequent disruption of monoaminergic and cholinergic inputs to the cortex. Pursuing this hypothesis further it is possible to amass evidence that the basal regions of the brain are vulnerable not only to thiamine lack but also to the direct toxic action of alcohol (Lishman 1990). Dendritic growth may stand to be compromised in the alcoholic subject, with a return to normal levels when prolonged abstinence has been assured. Other factors may also be involved, such as changes in protein or lipid synthesis (Harper 1989; Harper & Kril 1990). Laboratory evidence lends support to the possibility that a direct toxic action of alcohol on the brain may play a considerable role. Studies in mice and rats have shown that brain changes can be induced after a period of several months on a diet supplemented with alcohol (Riley & Walker 1978; Walker et al. Marked alterations in dendritic morphology were found in the hippocampal pyramidal neurones, dentate granular layers and cerebellar vermis, proceeding to cell degeneration and loss. These effects were produced despite the maintenance of good nutrition in all other respects. Detailed cell counts have indicated a 22% reduction in the number of neurones in the superior frontal cortex, along with reduction in the size of neurones in the motor and cingulate cortices (Harper et al. Abstinence then allows regrowth of dendritic branching and a return to normal thickness of the strata. Compared with normal controls, representative samples of alcoholics have been found commonly to have dilatation of the sulci, fissures and ventricles. Some 5070% of severe chronic alcoholics show indubitable evidence of cortical shrinkage or ventricular dilatation or both. Involvement of the frontal lobes of the brain has sometimes been particularly evident. The changes can be found in quite young alcoholics, appearing well within the first decade of alcohol abuse, although they become more marked in the older age groups studied. Planimetric measures of lateral ventricular size show on average some 50% enlargement compared with age-matched controls.
Such projections arise from the medial substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area medicine mound texas biltricide 600mg online, and these have been found to be particularly severely affected in parkinsonian patients with dementia (Rinne et al. Neuronal counts and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) levels have also proved to be reduced in the locus caeruleus in the presence of dementia, suggesting that diminished noradrenergic inputs to the cortex may make an additional contribution (Gaspar & Gray 1984; Chui et al. Dementia has emerged as exceptional with onset below the age of 50, even with disease of long duration, and it becomes commoner with later onset, especially after 70 years. Indeed the factor of age of onset has emerged as one of the firmest risk factors for the development of dementia. With age there is increasing likelihood of finding Alzheimer-type pathology in the cortex, and certain studies 764 Chapter 12 have suggested that this may play a major role in producing the dementia. However, further detailed studies have given conflicting results and this hypothesis is now regarded as uncertain (Jellinger & Riederer 1984; Gibb 1989). Rather they correlated with the extent of neuronal loss in the nucleus basalis of Meynert. This was always pronounced, with losses of up to 70% in the presence of parkinsonian dementia. Thus the cortical cholinergic deficits seemed not to be explicable in terms of cortical pathology, but more probably resulted from degeneration of cholinergic axons associated with the loss of cells in the Meynert nucleus. Such loss might itself be due to a pathological process analogous to that inducing changes in the substantia nigra. This striking set of observations has been both confirmed and refuted in other studies, as reviewed by Ross et al. These various possible contributions to dementia are discussed in detail by Dubois and Pillon (1992). It seems probable that many of the cognitive changes are largely due to subcortical pathology, with dopamine deficiency being compounded by loss of inputs from noradrenergic and cholinergic nuclei. Structural brain imaging has not contributed substantially to this cortical/subcortical debate. Third ventricular width and the intercaudate distance have also shown such associations, whereas the contribution of cortical atrophy usually disappears on controlling for age.
Ressel, 64 years: Surgical approaches have included selective division of cervical nerve roots, peripheral denervation, thalamotomy and even sternomastoid myotomy in very disabled patients, but the advent of treatment with botulinum toxin should reduce the need for such invasive procedures. To date studies have lacked sufficiently detailed clinical assessments to allow the differential contribution of macrovascular disease, hypertension, chronic hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinaemia and other factors to be determined and future detailed prospective studies are required to determine the relative contributions of each of these mechanisms. A simple linear regression analysis of the data-one conducted for each type of timber-yielded the following results (where y = stress and x = natural logarithm of number of cycles): y = 97. His "dread" of "the mystery of his own body," and his desire for "a new soaring impalpable imperishable being," ensured his ephebic, Shelleyan status.
Fasim, 54 years: Green lines indicate the parasympathetic fibers, red lines indicate motor fibers, and purple lines indicate visceral afferent fibers (taste). An effective vaccine (given on days 0, 7, and 30) is available and is indicated for summer travelers to rural Asia, where the risk can be as high as 2. Steroids remain one of the mainstays of treatment for the systemic effects of the disease and are also important in managing certain neuropsychiatric developments. Chemotherapy is more effective when there is less tumour present and therefore it is usually administered following radiotherapy or surgery; however, it can be used either concurrently or as initial therapy depending on the functional status of the patient (Mathieu & Fortin 2006).
Fabio, 24 years: Morihisa (1989) describes the strengths and limitations of such techniques and the findings that have emerged in relation to schizophrenia and developmental dyslexia, and uses have been described in relation to encephalopathies and attention deficit disorder. Reinforcement Schedules the presence or absence of reinforcing or punishing stimuli is just a part of the story. Haematological, biochemical and immunological tests should form part of the basic diagnostic armamentarium. Of course, sensory memory fades very quickly, and unless the information is attended to, it will be lost.